Have you ever wondered why your printed images don't look as sharp as they do on your computer screen? The answer lies in understanding DPI for printing, or dots per inch, and its impact on print quality. In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating world of DPI, debunk common misconceptions, and provide practical guidelines for optimizing your printing projects.
Short DPI Summary
DPI is essential for successful printing projects and should be considered alongside image resolution, file formats, and your printer type.
For marketing material print files, you should aim for a minimum of 300 DPI.
Image resolution, size, file format (lossless vs. lossy), and printer types all affect DPI & print quality.
Understanding the impact of these factors on DPI can help achieve optimal print quality without loss of detail or clarity.
Understanding DPI: The Basics
DPI, or dots per inch, is a crucial aspect of printing that determines the sharpness and detail of the final output. It's the measure of the density of dots in an image, which consequently affects its resolution and quality. But DPI is not the only factor that influences print quality – printer resolution, file formats, and printer types all play a role.
So, why is it important to understand DPI and its relationship with other factors? To achieve the best possible print results, especially when dealing with low-resolution images, it's essential to have a solid grasp of DPI and its implications.
Definition of DPI
DPI stands for dots per inch, a measurement used to assess the clarity and detail of an image on paper or the sensitivity of a computer mouse. It is a significant factor when printing and designing, as it determines the resolution or quality of the image. A low DPI value creates blurry images when printed.
The importance of DPI in printing cannot be overstated. It is a measure of the dots density in an image. Selecting the right DPI value is vital for the success of any print project, as higher DPI values result in better print quality, while lower DPI values can lead to pixelated or blurry prints.
DPI vs. PPI
DPI and PPI are often used interchangeably, but the two have a key difference. DPI, or dots per inch, refers to the number of printed dots within one inch of an image printed by a printer. On the other hand, PPI, or Pixels Per Inch, denotes the number of pixels within one inch of an image displayed on a digital screen. DPI and PPI are vital when working with medium-resolution images to ensure optimal print quality.
The DPI and PPI values necessary for various print applications differ depending on the size and type of the print. For instance, marketing materials usually necessitate higher DPI and PPI values than large-format prints. Ensuring the correct DPI and PPI values are used can help prevent blurry images in the final print.
Importance of DPI in Printing
DPI is critical in printing as it determines the sharpness and detail of the final printed product. Generally, increased DPI yields improved quality. But it's not just about the DPI value; factors such as image resolution and size, file formats, and printer types contribute to the final print quality. For instance, converting RGB images to CMYK is essential for printing on a four-color printing press, as CMYK is the color space used in printing.
Resolution, or the number of pixels in an image, directly influences the sharpness and detail of the printed product. By understanding the importance of DPI and other factors, you can achieve the best possible print results for your projects.
Factors Affecting DPI and Print Quality

To achieve the best possible print quality, it's essential to understand the factors that influence DPI and print quality. Image resolution and image size are two of the most important factors that influence print quality dpi. In this section, we'll discuss the impact of image resolution and size, file formats, and printer types on DPI and print quality.
Image Resolution and Size
Image resolution and size play a significant role in determining the final DPI and print quality. Image resolution is defined as the number of pixels in an image and has a direct effect on the print quality. Images with higher resolution will display more detail and will produce a higher quality print than images with lower resolution.
When working with images, it's important to consider the appropriate DPI for optimal print quality. Remember that increasing the size of an image does not increase its resolution. In fact, enlarging an image beyond its original resolution can result in pixelation, which leads to a loss of detail and quality in the final print.
File Formats: Lossless vs. Lossy
File formats play a crucial role in determining print quality. There are two primary file formats: lossless and lossy. Lossless formats, such as TIFF and PNG, retain all image data and yield a higher-quality print. Lossy formats, including GIF or JPEG files, compress the image data, resulting in a lower-quality print.
It's essential to choose the right file format for your printing needs. Lossless formats are recommended for printing to maintain color quality and contrast, while lossy formats may result in lower-quality prints. Keep in mind that smaller file sizes are beneficial for web use but may not be suitable for high-quality printing.
Printer Types: Inkjet vs. Laser
Printer types, such as inkjet and laser, can affect the final print quality. Inkjet printers are versatile and can produce quality prints with a wide range of DPI settings, making them suitable for various printing projects. However, the ink used in inkjet printers may cause seeping, which can reduce the dots per inch of a printed work.
On the other hand, laser printers are known for their speed and precision, making them suitable for high-volume printing with consistent DPI. Laser printers use a toner that does not seep into the paper, often resulting in a clearer image.
Likewise, professional printers ensure accurate DPI and color consistency. By carefully considering the type of printer best suited for your printing needs, you can achieve the best possible print quality.
DPI Guidelines for Different Print Applications

In this section, we'll explore the DPI guidelines for various print applications, such as marketing materials, large-format prints, and photographs. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your prints will look sharp and professional.
Marketing Materials
Marketing materials, such as brochures, flyers, and business cards, typically require a DPI of 150-300 for good print quality. The higher the DPI, the better the print quality will be, especially for small fonts, intricate barcodes, graphics, and photos. For smaller items or intricate design and detailed prints, 300 DPI is strongly advised.
Large-Format Prints
Large-format prints, such as posters, banners, and billboards, may require a higher DPI to maintain image quality at larger sizes. The DPI guidelines for large-format prints usually range from 100 to 300 DPI, with 300 DPI being the preferred resolution for optimal clarity.
When creating large-format prints, it's crucial to consider the DPI requirements and how they will affect the final print quality. By selecting the appropriate DPI for your large-format prints, you can ensure that your designs are impactful and maintain their quality, even when viewed from a distance.
Photographs
Photographs generally require a higher DPI for optimal print quality, often 300 DPI or more. The higher the DPI, the better the print quality will be, especially for images with fine details and textures. For professional magazine images or exhibition-quality artwork, a DPI of 600 or higher may be necessary.
By understanding the DPI requirements for photographs and selecting the appropriate DPI, your printed photos will be sharp, vibrant, and true to the original image. High-quality photo prints can make a lasting impression, serve as cherished keepsakes, or provide stunning artwork for your home or office.
Tips for Optimizing DPI and Image Resolution

In this section, we'll provide practical tips for optimizing DPI and image resolution. By following these guidelines, you can achieve the best possible print quality for your projects, whether you're printing marketing materials, large-format prints, or photographs.
Scanning Techniques
Proper scanning techniques can help maintain high DPI and image quality for printing. When scanning images, be sure to choose the appropriate resolution or dots per inch (dpi) for your project. Start with high-quality images and select the appropriate file type, such as JPEG or PNG.
Preserving color and sharpness is essential, especially when scanning images that will be edited. To do so, saving the scanned images as lossless TIF or EPS files is advisable. Following these scanning techniques ensures that your printed images maintain their quality and detail, even when enlarged or printed at high resolutions.
Image Editing
Image editing software can be used to adjust DPI and resolution, but care must be taken not to degrade image quality. When resizing images, it's important to use TIF or EPS files, and consider the appropriate DPI.
Remember that increasing the size of an image does not increase its resolution. In fact, enlarging an image beyond its original resolution can result in pixelation, which leads to a loss of detail and quality in the final print.
When selecting a file type, such as JPEG or PNG, consider the content and quality requirements of the image. Additionally, so long as no further scaling up is done, you can utilize compression techniques to reduce the file size without significantly impacting the image quality.
Following these image editing tips ensures that your printed images maintain their quality and detail, even when resized or printed at high resolutions.
File Conversion: RGB to CMYK

Converting digital images from RGB to CMYK is essential for accurate color reproduction in printing. RGB, or red, green, and blue, is the color space used for digital images displayed on screens. CMYK, or cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black), is the color space used for printing on a four-color printing press.
To ensure optimal print quality, converting images from RGB to CMYK before printing is recommended. RGB and CMYK color profiles are completely different. This conversion ensures that colors are accurately reproduced on the printed page and helps to prevent color shifts or inaccuracies. By following this file conversion technique, you can achieve the best possible print quality for your projects.
Note: Another popular way to ensure color matching when printing is using pantone colors. The Pantone system is a collection of over 1100 different colors that are all labelled. When you find the specific color that's just right for your project, it has a name and a number assigned to it. Printers that use this system read these numbers and are able to recreate the color.
Common DPI Misconceptions and Pitfalls
In this section, we'll address common misconceptions and pitfalls related to DPI, including pixelation, overcompensation, and misunderstanding DPI values. By understanding these misconceptions and pitfalls you can avoid common mistakes.
Pixelation
Pixelation occurs when an image is displayed or printed at an inadequate resolution, causing individual pixels to become visible and resulting in a blocky or blurry appearance. This visual artifact is often seen in low-resolution or improperly rendered images, where the image is enlarged beyond its original resolution, leading to a degradation of detail and quality.

To avoid pixelation, it's essential to work with the proper file types, high-resolution images, and ensure that they are resized appropriately for printing. By maintaining the correct resolution and DPI settings, you can achieve sharp, detailed prints without the unwanted effects of pixelation.
Overcompensation
Overcompensation refers to the practice of increasing DPI in software without improving the actual image quality. This can lead to a lack of detail and clarity in the final print, as the software merely alters the size of the dot without increasing the resolution of the image.
To avoid overcompensation, it's essential to work with high-resolution images and ensure that they are resized appropriately for printing. Additionally, be aware of the actual resolution of your images. Avoid lower-resolution images, and refrain from artificially increasing DPI values that may result in poor print quality. Considering what royalty-free images cost, it's a wise investment to opt for high-quality images and avoid low-resolution image usage to ensure optimal results.
Misunderstanding DPI Values
Misunderstanding DPI values can lead to poor print quality or unnecessarily large file sizes. It's a common misconception that higher DPI values always lead to improved print quality. However, the DPI value is just one of the many factors that affect print quality, and simply increasing DPI in a software may not result in better prints.
To avoid misunderstandings and pitfalls related to DPI values, it's crucial to have a solid grasp of DPI, its relationship with other factors, and its impact on print quality.
How to Choose the Right Printer for Your DPI Needs

Choosing the right printer for your DPI needs is essential for achieving optimal print quality. In this section, we'll discuss factors to consider when choosing the right printer for your needs. These include considering inkjet or laser printers, and selecting the best printer for your specific job.
Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers are versatile and can produce high-quality prints with a wide range of DPI settings, making them suitable for various printing projects. These printers utilize liquid ink to generate printed documents and are generally more affordable to acquire. However, the ink used in inkjet printers may cause seeping, which can reduce the dots per inch of a printed work.
When selecting an inkjet printer, consider factors such as print volume, desired DPI, and budget. Inkjet printers are affordable and work for printing high-resolution images, making them a popular choice for independent photographers and graphic designers.
Laser Printers
Laser printers are renowned for their speed and precision, making them suitable for high-volume printing with consistent DPI. These printers use a toner that does not seep into the paper, resulting in a clearer image. Laser printers may have a higher initial cost but usually have a lower overall cost of ownership, making them a popular choice for businesses and offices.
Consider factors such as print volume, desired DPI, and budget when selecting a laser printer. Laser printers are ideal for printing text and graphics, making them a popular choice for office documents and marketing materials.
Selecting the Best Printer for Your Needs
When selecting a printer to meet your DPI requirements, factors to consider include the type of project, resolution, cost, size, and ink or toner type. Basic printers typically provide a sufficient resolution for most documents, while photo printers are designed to produce high-quality prints.
By carefully considering the type of printer best suited for your printing needs, you can achieve the best possible print quality and DPI. Whether you're printing marketing materials, large-format prints, or photographs, understanding DPI and selecting the right printer will ensure that your projects look stunning and professional.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding DPI and its impact on print quality is crucial for the success of your printing projects. From differentiating between DPI and PPI to selecting the right printer and optimizing image resolution, this article has provided practical guidelines to help you achieve the best possible print quality. Avoiding DPI misconceptions and your printed materials will be sharp, visually appealing, and make a lasting impression on your target audience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is 300 or 600 DPI better for print?
For prints, 600 DPI offers higher resolution and thus better quality results, while 300 DPI is sufficient and works for many print projects.
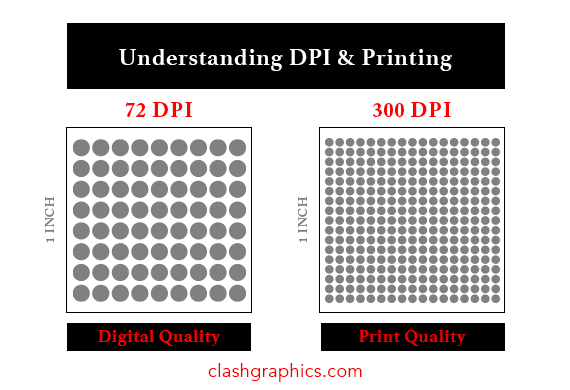
Should I print 72 or 300 DPI?
For the best print quality, you should print your image at 300 DPI for crisp and clear results.
A lower resolution of 72 PPI will appear pixelated and blurry.
What is the difference between DPI and PPI?
DPI is a measure of printed dots per inch, while PPI is a measure of pixels per inch, making them useful for different types of images.
What factors affect DPI and print quality?
DPI and print quality are largely determined by the resolution of the image, the file format used, and the type of printer employed.
Different printers have different capabilities, so it's important to understand their differences. For example, inkjet printers are capable of producing higher-resolution prints than laser printers. Additionally, the type of paper used can also affect the print quality.
How can I optimize DPI and image resolution?
Optimizing DPI and image resolution can be achieved by employing proper scanning techniques, using image editing applications, and converting RGB files to CMYK.
Clash Graphics Print Shop Atlanta Flyer Printing
2233 Peachtree Rd NE Ste 202 Atlanta, GA 30309
(678) 235-3464
To view the original version on Clash Graphics, visit: https://www.clashgraphics.com/printing-tips/understanding-dpi-for-printing-how-resolution-affects-print-quality/
No comments:
Post a Comment